Real time eye gaze tracking demo 1
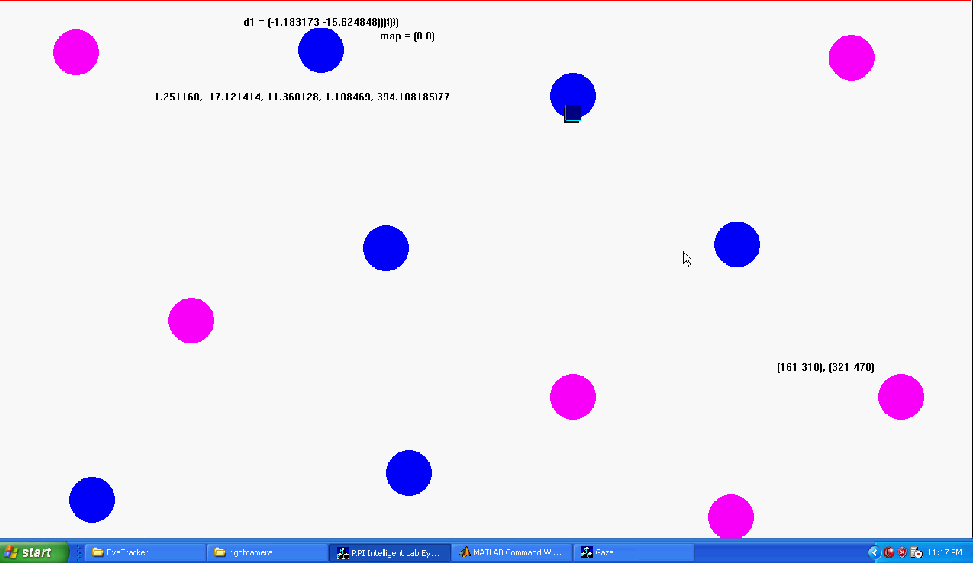
This demo shows that as the user is looking at different reference points around the screen, the gaze point can be estimated accurately via the proposed gaze tracking technique. The static cirles with different colors represent the reference objects that the user will look at. The blinking square that changes locations is the estimated gaze point, representing where the user is looking at.
 Zhiwei Zhu, Qiang Ji, "Eye Gaze Tracking Under Natural Head Movements", International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR05), San Diego, CA, June 2005.
Zhiwei Zhu, Qiang Ji, "Eye Gaze Tracking Under Natural Head Movements", International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR05), San Diego, CA, June 2005.