|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Active Information Fusion |
Active Information Fusion with Dynamic Bayesian Networks Many information fusion applications are often
characterized by a high degree of complexity because 1) data are often acquired
from sensors of different modalities and with different degrees of uncertainty;
2) decisions must be made timely; and 3) the world situation evolves over time.
To address these issues, we propose an information fusion framework based on
dynamic Bayesian networks (DBNs) to provide active, dynamic, purposive and
sufficing information fusion in order to arrive at a reliable conclusion with
reasonable time and limited resources. The proposed framework is well suited to
applications where the decision must be made efficiently and timely from
dynamically available information of diverse and disparate sources.
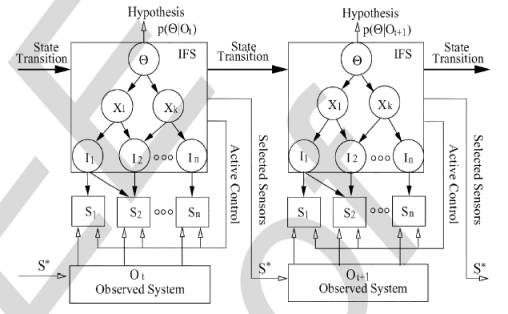
The above figure shows a functional view of active information fusion, in which the information fusion system (IFS) is a Bayesian network consists of hypotheses Q , intermediate variables H, information variables X, and sensors S. The active information fusion generally proceeds in four stages at each time instant: (1) Scheduling: based on the current system state to determine the optimal subset of sensors to be activated at the next time step t+1; (2) Observation: Obtain observations from the selected optimal sensor set; (3) Inference: compute the posterior probability of Q giving the observations by using DBN inference algorithms; (4) Decision-making: make a decision if the certainty in the current solution is sufficiently high. Otherwise, start over and reschedule sensors for future observations. |
Introduction
|
|
Summary
|
|
Demos
|
|
Publications
|
|
BN
Resources
|
|
|
|
|